AWS DynamoDB is fully managed NoSQL database service. You can create tables that can store data and revertive data from them. DynamoDB being fully managed service it can be auto scaled up/down, can perform on demand backup & even recover an accidentally deleted table within 35 DAYS. AWS DynamoDB the data store on SSD & replicated across Availability zone in a particular AWS region.
At the core the DynamoDB is composed of
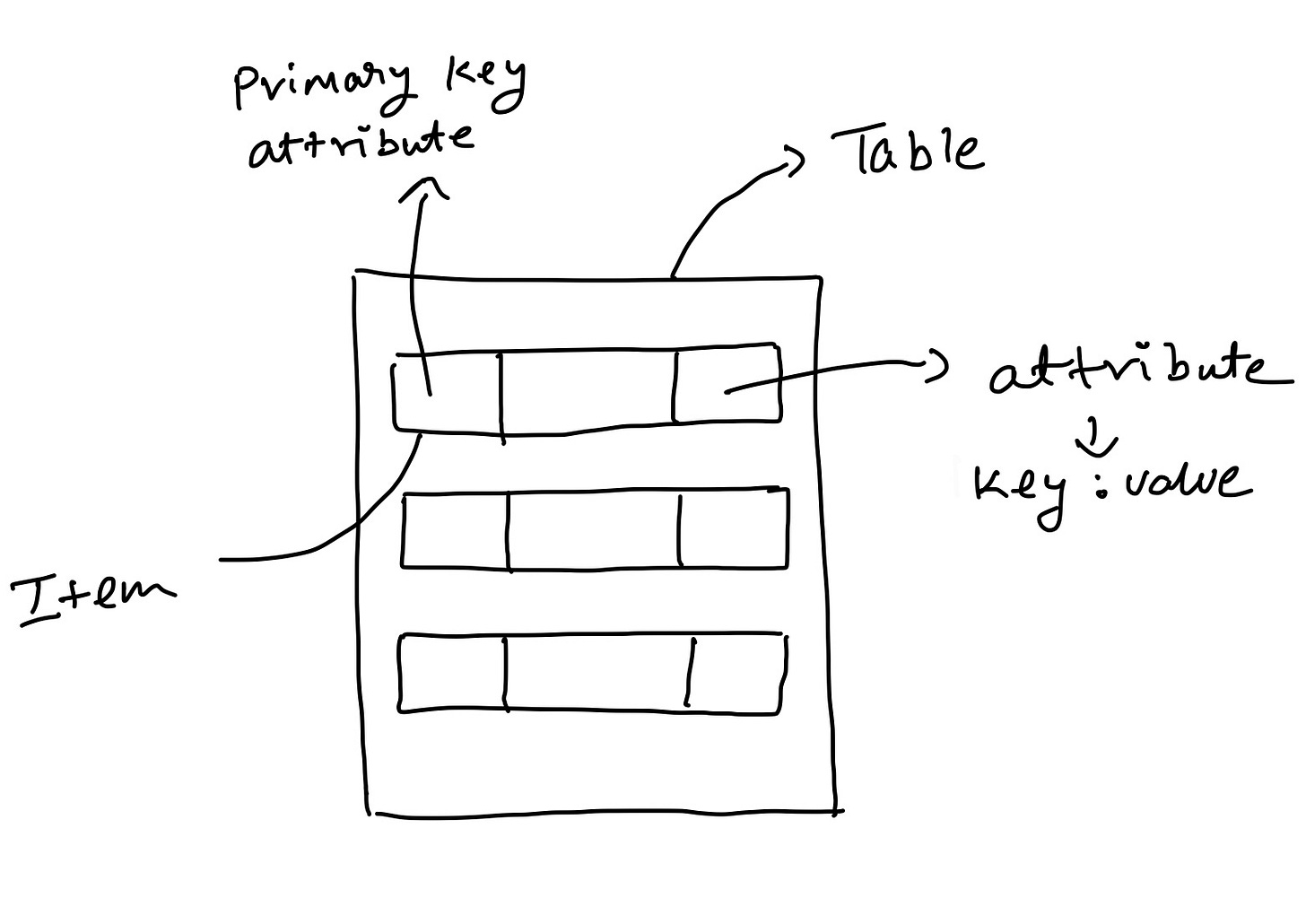
Table : Simply a table is collection of items
Item : An Item is a collection of attributes
Attribute : It is a fundamental entity which has a name and a value. An attribute cannot be broken down further.
DynamoDB uses Primary Keys to uniquely identify each item in the table and also supports secondary indices.
[A picture is worth thousand words]
[Lets dive deep in to each of these topics …]
Item
A item is simply a collections of attributes.
For performance reasons in DynamoDB each item size is capped at 400KB. And size of attribute can be anything not exceeding 400KB
Attribute
An attribute is the actual data you want to store. Each attribute has name and a value. An attribute values can be of the following type
Scalar Type : A scalar attribute can have a single value and can be a string, number, boolean or null
Document Type : A document type represent complex structures with nested attributed. These can be either a list and maps. These types can be nested within each other.
List → A list is ordered collection of values, like a JSON array
Map → Maps can store unordered collection of key value pairs, like a JSON object
Set Type : A set is homogeneous collection of number, string or binary values, where each element is unique element. In dynamoDB a empty is not allowed and order in elements are store is not preserved ( a thumb rule is we shouldn’t be dependent in the order). Being said this, a set can contain elements with empty values.
Primary Keys
To uniquely identify an entity, DynamoDB uses Primary Keys. In DynamoDB it is mandate to specify Primary Keys when creating a table. The primary keys should be a scalar type attribute, which should uniquely identify an item.
DynamoDB supports two type of Primary Keys
Partition Key : A partition keys is composed on only one attribute.
In table with Partition Key no two items can have the same partition key value. DynamoDB uses the partition key value as input to an internal hash function. The output from the hash function determines where item will be stored. Partition key is also referred as Hash attribute.
Composite Key : A composite key is compose of two attributes
Partition Key
Sort Key (also referred as Range attribute)
In Composite Primary Key it is possible for multiple items to have the same partition key value, these items must have different sort key values. All item with same partition keys are store together, sorted by sort key value.
Secondary Indices
DynamoDB also support Secondary Indices. Secondary Indices are data structures which contain subset of attribute along with along with an alternate keys. You can create upto fives Secondary Indices for a table. Secondary Indices allow you to query the table with alternate keys. In general it is not recommended to have Secondary Indices (for performance reasons), but secondary index should be used for efficient access of data using attributes other than primary keys.
Every secondary index is associated with exactly one table, from which it obtains its data. This is called the base table for the index. When you create an index, you define an alternate key for the index. You also define the attributes that you want to be copied, from the base table into the index. You can then query or scan the index just as you would query or scan a table.
DynamoDB Stream
DynamoDB Stream captures the item level data modification events in DynamoDB tables. The data about these evens appear in stream in the order they have occurred. An event is captured in form of a stream record. Each stream record occurs once in the stream and has be TTL of 24hrs within consumers can process these stream records.
DynamoDB Stream write stream records when an
Item is Added → The stream record consists of snapshot of all the attribute of item which was added.
Item is Updated → The stream record consists of attribute snapshot of attributes before and after the update has occurred
Item is Deleted → The stream record consists of snapshot of all the attribute of item which was deleted.
DynamoDB streams can be leverage by for use cases like
Data replication
Data analysis
Triggers
Thats not it, there’s lots to explore in DynamoDB … thats for another article.

Hey Readers, Leave out comments on topic you want to explore further